
Relegation from a top-tier football league represents one of the most significant financial threats to a professional football club. This case study examines the monetary costs associated with relegation in Europe’s five major football leagues: the English Premier League (EPL), La Liga (Spain), Bundesliga (Germany), Serie A (Italy), and Ligue 1 (France) over the last five years/seasons.
Our analysis reveals that while all relegated clubs face substantial revenue losses across broadcasting rights, commercial deals, and matchday income, the specific financial impact varies significantly between leagues, largely influenced by the presence and structure of ‘parachute payments.’ The Bundesliga, notably, stands out for its lack of such payments, leading to a more immediate and severe financial shock upon relegation. Understanding these diverse financial landscapes is crucial for clubs, investors, and governing bodies to better prepare for and mitigate the economic consequences of dropping out of elite competition.
1. Introduction: The Perilous Drop from Elite Football
In the fiercely competitive world of European football, the distinction between a top-tier club and one relegated to a lower division is not merely about sporting prestige; it carries profound and often devastating financial implications. The ‘Big Five’ leagues—the English Premier League, Spain’s La Liga, Germany’s Bundesliga, Italy’s Serie A, and France’s Ligue 1—represent the pinnacle of club football, commanding massive global audiences, lucrative broadcasting deals, and significant commercial opportunities. For clubs operating within these leagues, maintaining top-flight status is paramount to their economic survival and growth.
Relegation, the process by which underperforming teams are demoted to a lower division, triggers a cascade of financial penalties. These include a drastic reduction in broadcasting revenue, diminished sponsorship appeal, lower matchday income due to reduced attendance and ticket prices, and a decrease in player market values. The sudden drop in income can lead to severe financial instability, forcing clubs to sell key players, cut operational costs, and even face administration or bankruptcy in extreme cases.
This case study aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the monetary costs of relegation across these five major European leagues over the past five years/seasons. By analyzing available data on revenue losses and the mitigating effects of ‘parachute payments’ (financial support provided to relegated clubs), we seek to quantify the economic impact and highlight the varying financial landscapes that clubs navigate upon demotion. The insights gained will underscore the critical importance of sporting performance in safeguarding a club’s financial future.
2. The Financial Impact of Relegation Across Europe’s Top 5 Leagues
The financial consequences of relegation are multifaceted, impacting various revenue streams for a football club. While the general trend is a significant decline in income, the specific magnitude and the mitigating factors, such as parachute payments, differ considerably across the major European leagues.
2.1. English Premier League (EPL)
The English Premier League is widely regarded as the wealthiest football league globally, primarily due to its colossal broadcasting deals. Consequently, relegation from the EPL represents arguably the most severe financial blow in European football.
- Revenue Reduction: Clubs relegated from the Premier League face a drastic reduction in revenue. Some estimates suggest a direct revenue loss of up to £50 million in the first year alone [1]. Beyond this immediate impact, relegated clubs experience a significant decline in commercial income, with an average fall of £6 million (45%) from £14 million to £8 million in the last five years for those dropping out of the top flight [2]. The primary driver of this loss is the forfeiture of the substantial broadcast revenue, which can be around £200 million per year for each Premier League team [3].
- Parachute Payments: To mitigate the financial shock and help clubs adjust to the lower revenue environment of the Championship (the second tier of English football), the Premier League provides ‘parachute payments.’ These payments are distributed over three years, gradually decreasing in value: 55% of the broadcast revenues in the first year after relegation, 45% in the second, and 20% in the third [4]. In recent seasons, this has amounted to approximately £41 million in the first year [5]. These payments are part of a larger £1.6 billion solidarity fund designed to support the English Football League (EFL) [6]. Despite these payments, the aggregate 3-year upper loss limit for a club dropping from the Premier League to the Championship is a staggering £83 million at the end of the first season [7].
2.2. La Liga (Spain)
La Liga, Spain’s top football division, also presents significant financial challenges for relegated clubs, though its parachute payment system differs from the EPL.
- Revenue Loss: Relegation from La Liga leads to substantial financial losses, primarily from reduced TV broadcasting rights, diminished sponsorship deals, and lower matchday income [8]. Specific examples from recent seasons highlight the immediate impact: clubs like Cadiz faced a loss of €24 million, Almeria €25.8 million, and Getafe €27.7 million upon relegation. Elche, already relegated, experienced a €25 million drop in income [9].
- Parachute Payments: La Liga’s parachute payments are structured based on a club’s tenure in the top division. For instance, a club that has spent at least three of the last four seasons in La Liga receives €25 million. Clubs with less time in the top flight receive smaller amounts [10, 11]. These payments are typically provided for one year and average around £12 million [12]. While these payments offer some relief, they are generally less substantial and cover a shorter period compared to the EPL’s system, potentially leading to a quicker and more pronounced financial adjustment for relegated clubs.
2.3. Bundesliga (Germany)
The Bundesliga stands out among the top five European leagues for its unique approach to financial support for relegated clubs.
- Revenue Loss: Relegation from the Bundesliga results in significant financial losses, particularly in broadcasting revenue [13]. A notable example is Werder Bremen, which absorbed a €40 million loss following its relegation to the 2. Bundesliga [14]. The absence of a direct parachute payment system means that the financial impact is often more immediate and severe for clubs dropping out of the top tier.
- No Parachute Payments: Unlike the other major leagues, the Bundesliga does not distribute specific parachute payments to relegated clubs [15]. This is attributed to a different distribution model for broadcasting revenues, which aims to create a more equitable financial landscape across its divisions. While this system may foster greater financial stability within the league as a whole, it means that relegated clubs face the full brunt of reduced income without the cushioning effect of multi-year financial aid.
2.4. Serie A (Italy)
Serie A, Italy’s premier football league, also employs a parachute payment system to help clubs manage the transition to a lower division.
- Revenue Loss: Relegation from Serie A leads to millions in lost revenue from TV rights, sponsorships, and player valuations [16]. Clubs can experience substantial drops in overall income [17].
- Parachute Payments: Serie A introduced its parachute payment system in 2009. The amount received depends on a club’s recent history in the top flight: clubs that have been in Serie A for the last three seasons (or three of the last four) receive €25 million. Clubs with less recent top-flight experience receive €15 million (Tier B) or €10 million (Tier A) [18, 19]. These payments are primarily for the first season after relegation, with some smaller amounts potentially extending into a second season [20].
2.5. Ligue 1 (France)
Ligue 1, the top tier of French football, also sees significant financial repercussions for relegated clubs, often characterized by drastic budget reductions.
- Revenue Loss: Relegation from Ligue 1 typically results in a substantial decrease in a club’s operational budget. For instance, Reims, with an estimated €60 million budget in Ligue 1, anticipated their budget dropping to around €20 million upon relegation to Ligue 2 [21]. This represents a two-thirds reduction in financial capacity. French clubs collectively experienced significant operating losses, with projections of €1.2 billion for the 2024/25 season across Ligue 1 and Ligue 2, highlighting the precarious financial state of many clubs [22].
- Parachute Payments: While Ligue 1 does have mechanisms to support relegated clubs, the research indicates that the focus is often on the drastic budget cuts and financial struggles rather than a clearly defined, multi-year parachute payment system comparable to the EPL. The financial support aims to ease the transition, but the immediate impact on a club’s budget is severe [23].
Visualizations of Relegation Costs
To further illustrate the financial landscape of relegation across these leagues, the following charts provide a comparative overview of estimated annual revenue loss and first-year parachute payments.
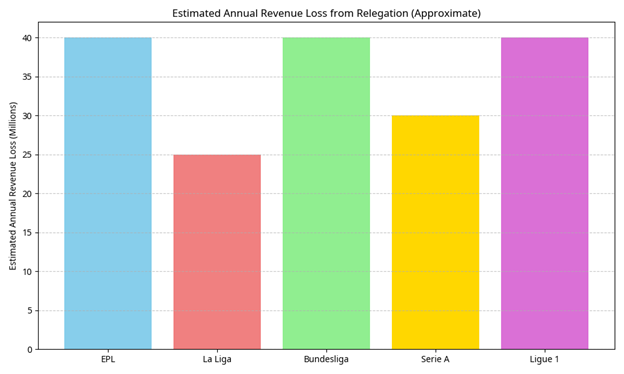
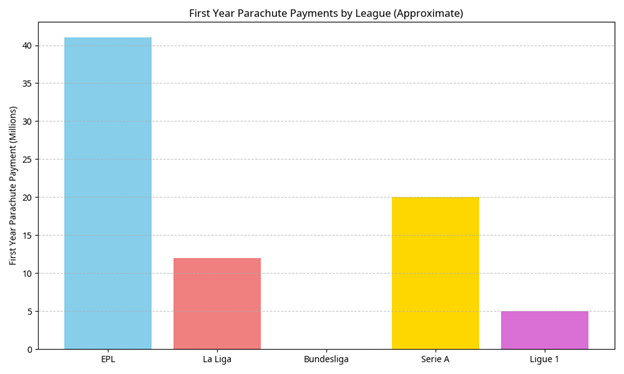
These visualizations underscore the varying degrees of financial impact and support mechanisms across Europe’s top football leagues, with the Bundesliga notably lacking parachute payments, making its relegated clubs particularly vulnerable to immediate financial downturns.
3. Conclusion: Navigating the Financial Abyss of Relegation
Relegation from Europe’s top five football leagues represents a profound financial challenge for clubs, far exceeding a mere sporting setback. The analysis of the English Premier League, La Liga, Bundesliga, Serie A, and Ligue 1 over the past five years reveals a consistent pattern of substantial revenue loss across broadcasting, commercial, and matchday income streams.
While the precise figures and mechanisms vary, the overarching message is clear: maintaining top-flight status is not just about sporting ambition but is a critical determinant of a club’s financial health and long-term sustainability.
The presence and structure of ‘parachute payments’ emerge as a key differentiator in how clubs manage the immediate aftermath of relegation. Leagues like the EPL and Serie A offer significant financial cushions, designed to soften the blow and provide a transitional period for clubs to adjust their financial models.
However, even with these payments, the reduction in revenue is substantial, often necessitating player sales, wage reductions, and strategic restructuring. The Bundesliga’s unique absence of parachute payments highlights a more abrupt and potentially more severe financial shock, forcing clubs to adapt almost immediately to a significantly reduced income.
For clubs, understanding the specific financial landscape of their league is paramount. Proactive financial planning, robust commercial strategies, and a strong focus on sporting performance are essential to mitigate the risks associated with relegation.
For governing bodies, the varying impacts of relegation across leagues raise questions about competitive balance, financial fair play, and the long-term health of the football pyramid. As the financial stakes in football continue to escalate, the ability to navigate the perilous drop of relegation will remain a defining challenge for clubs across Europe.
References
[1] League Relegation Explained – Number Analytics. (2025, June 23). [https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/league-relegation-explained](https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/league-relegation-explained)
[2] Impact of Relegation from the Premier League 2022/23 – The Swiss Ramble. (2023, June 4). [https://swissramble.substack.com/p/impact-of-relegation-from-the-premier](https://swissramble.substack.com/p/impact-of-relegation-from-the-premier)
[3] Question about the economics of relegation… : r/PremierLeague. (2023, April 12). [https://www.reddit.com/r/PremierLeague/comments/12iulcd/question_about_the_economics_of_relegation/](https://www.reddit.com/r/PremierLeague/comments/12iulcd/question_about_the_economics_of_relegation/)
[4] The financial catastrophe of relegation from the Premier League. (2023, May 31). [https://www.bishopandsewell.co.uk/2023/05/31/the-financial-catastrophe-of-relegation-from-the-premier-league/](https://www.bishopandsewell.co.uk/2023/05/31/the-financial-catastrophe-of-relegation-from-the-premier-league/)
[5] Parachute payments and the ‘yo-yo’ club phenomenon … – BBC. (2022, June 23). [https://www.bbc.com/sport/football/61809071](https://www.bbc.com/sport/football/61809071)
[6] Leicester City and Southampton tap into £1.6bn fund as relegation … – EFL Analysis. (2025, April 23). [https://eflanalysis.com/news/championship-parachute-payments-explained/](https://eflanalysis.com/news/championship-parachute-payments-explained/)
[7] The “R” word and its financial consequences – The Esk. (2023, April 29). [https://theesk.org/2023/04/29/the-r-word-and-its-financial-consequences/](https://theesk.org/2023/04/29/the-r-word-and-its-financial-consequences/)
[8] League Relegation Explained – Number Analytics. (2025, June 23). [https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/league-relegation-explained](https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/league-relegation-explained)
[9] The cost of relegation for each of the seven clubs in the La Liga … – Football Espana. (2023, May 19). [https://www.football-espana.net/2023/05/19/the-cost-of-relegation-for-each-of-the-seven-clubs-in-the-la-liga-relegation-battle](https://www.football-espana.net/2023/05/19/the-cost-of-relegation-for-each-of-the-seven-clubs-in-the-la-liga-relegation-battle)
[10] Mike on X: “In La Liga, parachute payments are paid out based on …” (2025, February 13). [https://x.com/Mike_RMCF/status/1890111634128953540](https://x.com/Mike_RMCF/status/1890111634128953540)
[11] What Are The Parachute Payments For Teams Relegated … – Forbes. (2024, May 27). [https://www.forbes.com/sites/adamdigby/2024/05/27/what-are-the-parachute-payments-for-teams-relegated-from-serie-a/](https://www.forbes.com/sites/adamdigby/2024/05/27/what-are-the-parachute-payments-for-teams-relegated-from-serie-a/)
[12] Spanish football – in a league of its own – Pitch32. (2021, May 14). [https://pitch32.com/spanish-football-in-a-league-of-its-own/](https://pitch32.com/spanish-football-in-a-league-of-its-own/)
[13] TV money in the 2. Bundesliga: how much does your club pocket? – Yahoo Sports. (2025, July 8). [https://sports.yahoo.com/article/tv-money-2-bundesliga-much-071100287.html](https://sports.yahoo.com/article/tv-money-2-bundesliga-much-071100287.html)
[14] Werder CEO: “Covid and relegation were disastrous, but they … – LinkedIn. (2025, January 19). [https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/werder-ceo-covid-relegation-were-disastrous-sharpened-our-frusf](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/werder-ceo-covid-relegation-were-disastrous-sharpened-our-frusf)
[15] Broadcasting breakdown: the European Big 5 – Tifosy. [https://www.tifosy.com/insights/broadcasting-breakdown-the-european-big-5-3481](https://www.tifosy.com/insights/broadcasting-breakdown-the-european-big-5-3481)
[16] Serie A relegation battle : current standings, situation and playoff … – DeepBetting.io. (2025, April 29). [https://deepbetting.io/serie-relegation-battle-current-standings-situation-playoff-scenarios/](https://deepbetting.io/serie-relegation-battle-current-standings-situation-playoff-scenarios/)
[17] Serie A general growth and the impact on matchday attendance – Four Nations Football. (2025, February 6). [https://www.fournations.football/post/serie-a-general-growth-and-the-impact-on-matchday-attendance](https://www.fournations.football/post/serie-a-general-growth-and-the-impact-on-matchday-attendance)
[18] What Are The Parachute Payments For Teams Relegated … – Forbes. (2024, May 27). [https://www.forbes.com/sites/adamdigby/2024/05/27/what-are-the-parachute-payments-for-teams-relegated-from-serie-a/](https://www.forbes.com/sites/adamdigby/2024/05/27/what-are-the-parachute-payments-for-teams-relegated-from-serie-a/)
[19] Serie A: How Much Is the “Parachute Payment”? – Calcio Deal. (2025, May 14). [https://calciodeal.com/en/serie-a-how-much-is-the-parachute-payment/](https://calciodeal.com/en/serie-a-how-much-is-the-parachute-payment/)
[20] [PDF] Parachute payments in English football: Softening the landing or … – Shura. (n.d.). [https://shura.shu.ac.uk/17115/3/Wilson-ParachutePaymentsInEnglishFootball%28AM%29.pdf](https://shura.shu.ac.uk/17115/3/Wilson-ParachutePaymentsInEnglishFootball%28AM%29.pdf)
[21] Cost of Reims’ relegation to Ligue 2 revealed – Yahoo Sports. (2025, June 3). [https://sports.yahoo.com/article/cost-reims-relegation-ligue-2-103600033.html](https://sports.yahoo.com/article/cost-reims-relegation-ligue-2-103600033.html)
[22] The DNCG, the organization responsible for overseeing the financial … – Reddit. (2025, February 4). [https://www.reddit.com/r/soccer/comments/1ihe4xx/the_dncg_the_organization_responsible_for/](https://www.reddit.com/r/soccer/comments/1ihe4xx/the_dncg_the_organization_responsible_for/)
[23] Ligue 1’s two-faced truth: European success is masking financial ruin – The Guardian. (2025, April 24). [https://www.theguardian.com/football/2025/apr/24/ligue-1-finances-champions-league-dazn-analysis](https://www.theguardian.com/football/2025/apr/24/ligue-1-finances-champions-league-dazn-analysis)

Leave a Reply